As of 2015, companies in the United States reported annual combined losses exceeding $525 million (USD) due to cyber crime. The majority of these losses stem from malicious code and denial of service attacks. [1]
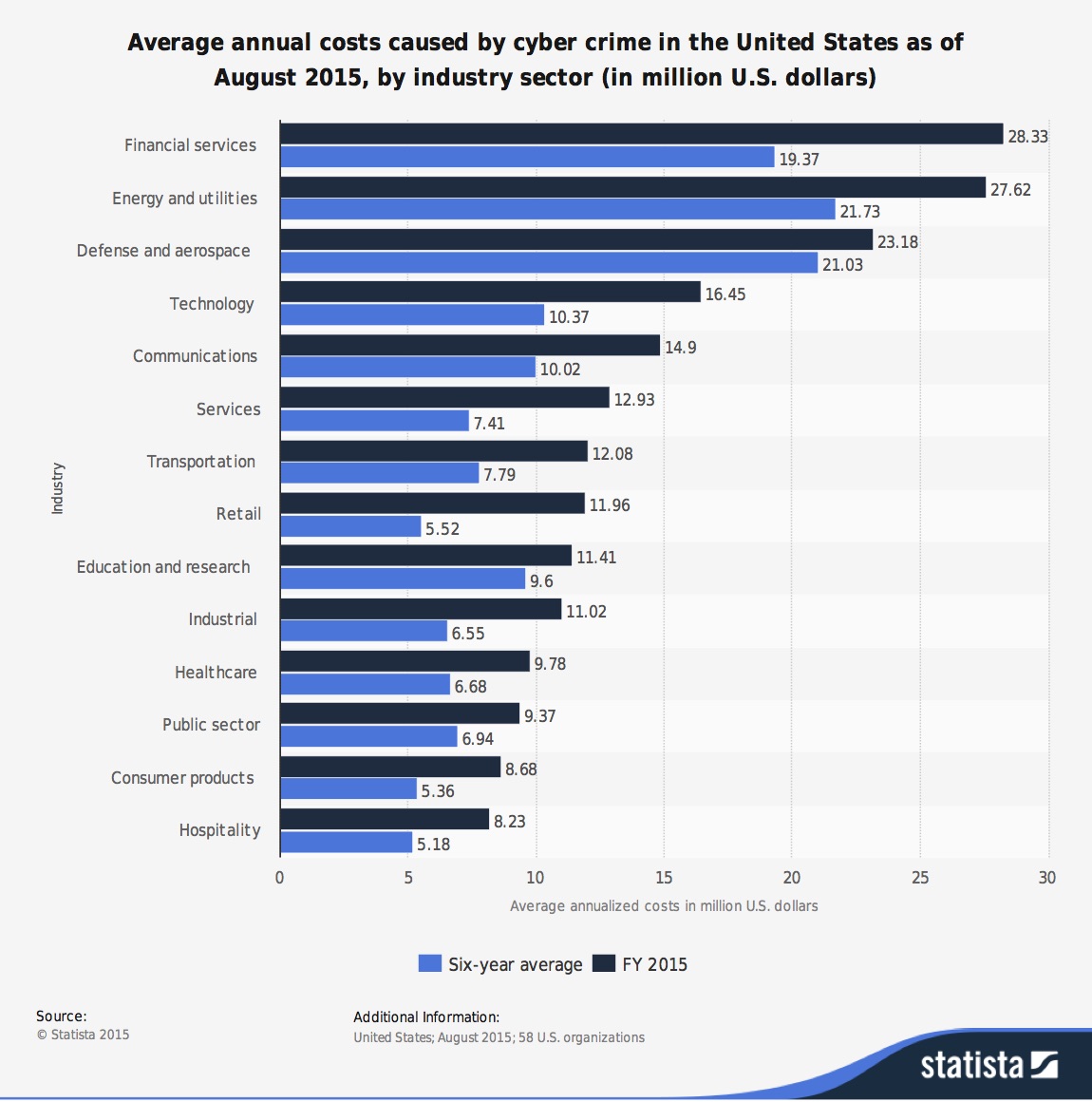
Not only are banks at risk of the threat of security breaches, U.S. financial institutions experience some of the highest average annual costs caused by cyber crime of any industry. In fact, for FY 2015, this sector was hit with $28.33 million in costs – the highest hit overall for the year. And cyber crime activity continues to increase exponentially. The financial industry is a perfect example – the 2015 cost is almost $10 million higher than its six-year average.
It’s never been more important for banks to address the current and future potential risks to its systems and sensitive data.
Protecting these systems poses a complex challenge. Banks must monitor and minimize risks on many fronts. At the same time, they must institute comprehsnsive, agile protection from cyber criminals, technology innovation, human error, and even natural disasters. For that reason, cybersecurity should be considered an enterprise-wide concern that deserves attention from the entire C-suite. We’re beginning to see prioritization – in fact, in 2016, the nation’s top CFOs listed cyber risk as their number two priority.
For CFOs, bank management and board members, it needs to be a top priority. With that in mind, our expert cyber security team has prepared this checklist of Key Risk Areas to help you start to ask the questions necessary to ensure your organization is well-protected.
- The Human Factor: Human error and oversight are the most common causes of security breaches – and education is key to mitigating them. Employees who are not adequately trained can expose your bank to breaches by malicious attacks, phishing, scams, and even disgruntled employees. Assert everyone’s role in protecting the bank. Engage HR to train employees on cybersecurity and data protection procedures so they know how to be more careful and aware of the right procedures to protect the bank’s IT assets.
Ask this: Do your employees understand the importance of their role in protecting the bank?
- Access Management: Business systems are more interconnected than ever, requiring a thoughtful and detailed approach to access policies, procedure and management to protect sensitive data. Keep track of the users who access your systems and enforce regular password changes for users.
Ask this: Who has access to your systems? Is your bank managing this carefully?
- Security Policies and Procedures: If your systems and critical data are compromised, the bank is in danger of interrupted business, lost customers, and even personal liability. Accountability requires clear security policies and guidelines, along with actionable plans and procedures to address your unique situation.
Ask this: Do you have a plan to protect your bank? If a breach happens, do you have a recovery plan?
- Network Security: Internet-facing and internal portions of your network are targets for criminals who see your systems as breachable ‘attack surfaces’ connected to valuable data. Vulnerability scans are a first step, but they don’t tell the whole story. Banks need specialists to test external and internal networks the way hackers do – aggressively, creatively and persistently. Then prioritize your action plan and make the right changes.
Ask this: Is your network susceptible or vulnerable to security threats? Do you run vulnerability scans or penetration tests? What about your hardware – is it configured to provide protection and are these configurations up-to-date?
- Operating System and Application Security: Keeping the latest protections in place is necessary to defend your bank from attack. Almost daily, vendors become aware of and distribute patches for vulnerabilities in applications and operating systems. With internal, custom applications you are not able to take advantage of the vulnerability lifecycle. Enlist experienced security researchers to find and repair vulnerabilities in your software. Even if you can’t fix a vulnerability, you can structure your network and layer protections around known weak points to protect your data.
Ask this: Are you installing the patches that are critical to the security of your software?
- Data Encryption: Regulations and best practices continue to broaden the scope of what data must be encrypted. Mobile use is driving more data to reside outside the protection of central servers and encryption. Banks must consider encryption for data that is at rest on a system, as well as in transit between systems.
Ask this: Do you know what data is being encrypted to protect it from security breach? Is the right data being encrypted?
- Third Party Relationships: More than 60% of data breaches are linked to a third party vendor. When outside partners and vendors connect to critical systems through your supply chain and other business-to-business relationships, it increases the security risks in your systems. Third parties that interact with your systems must have security practices that meet or exceed your own. Monitoring these vendors can be challenging and time-consuming. Put the expertise in place to help you manage this significant security risk.
Ask this: Do your vendor and business partners meet your security standards?
- Disaster Recovery: Crisis requires a proactive approach to protecting your IT environment and minimize data loss and damage. Often, the security of a disaster recovery environment is not as secure as your production site. Backing up your data without carefully considering how that backup is transmitted, stored, and recovered can expose your data to additional vulnerability. If a negative event does happen, you need a restore and recovery plan as well as incident response to determine why the outage occurred and take precautions against future risk.
Ask this: Does your bank plan for the worst? Where do your backups reside? Did you know that your backup data can be a prime target for attackers?
Cybersecurity affects every level of the bank. Your entire executive team must work together to protect sensitive data, customer information, network operations, competitive secrets and business continuity. We can help you fill in the checklist and keep your bank from becoming a cyber threat statistic. Contact us now.
Join the conversation and receive updates of new posts:
[1] Statista, 2015



Leave A Comment